Zirconia blocks represent a breakthrough in modern dentistry, offering a myriad of benefits for patients and practitioners alike. Here's a closer look at what zirconia blocks are and how they have transformed the landscape of restorative dentistry:
1.What are Zirconia Blocks?
Zirconia, scientifically known as zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), is a mineral classified within the silicates class. Its unique composition contributes to outstanding mechanical properties, including high flexural strength (>1400 MPa), impressive hardness (1200 HV), and a robust Weibull module of 15.84. These characteristics make zirconia an ideal material for dental applications.
Zirconia blocks are ceramic materials crafted from zirconia, specifically tailored for use in dentistry. They are utilized in the fabrication of various dental prosthetics, such as crowns, bridges, and dental implants. Notably, zirconia blocks exhibit exceptional biocompatibility, ensuring compatibility with oral tissues. Furthermore, they are non-toxic and exceptionally durable, rendering them suitable for long-term dental restorations.
- Late 20th Century: Zirconia made its debut in dentistry during the late 20th century, primarily in the form of zirconia cores for dental crowns. These cores were often layered with porcelain to achieve desired aesthetic outcomes.
- Early 2000s: The advent of Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology catalyzed the widespread adoption of zirconia in dentistry. The introduction of monolithic zirconia restorations marked a significant advancement, offering solutions characterized by strength and biocompatibility.
- Mid-2000s: Colored zirconia blocks emerged, allowing for the creation of more natural-looking dental restorations. These blocks were pre-shaded to match the diverse hues of natural teeth, enhancing aesthetic outcomes.
- Late 2000s to Early 2010s: High-translucency zirconia blocks revolutionized aesthetic dentistry, rivaling traditional porcelain restorations in their ability to mimic natural tooth appearance. These blocks enabled enhanced light transmission, resulting in restorations with a lifelike appearance.
- Present Day: Multi-layer zirconia blocks have ushered in a new era of dental restoration. These innovative blocks feature varying levels of color and translucency within the same block, allowing for highly customized and aesthetically pleasing results that closely resemble natural dentition.
Conclusion:
The development of zirconia blocks has redefined the field of restorative dentistry, offering a harmonious blend of strength, biocompatibility, and aesthetics. As technology continues to progress, the properties and applications of zirconia in dentistry are poised for further enhancements, promising continued innovation and excellence in patient care.
2.Zirconia is widely used in various industries.
Zirconia, with its exceptional properties, finds extensive application across various industries, each benefiting from its unique characteristics. Here's a breakdown of the key areas where zirconia is utilized:
Dentistry: Zirconia plays a pivotal role in modern dentistry, serving as a cornerstone material for restorative and prosthetic procedures. From crowns and bridges to implant abutments and full-arch implant-supported prostheses, zirconia's mechanical robustness, biocompatibility, and natural appearance make it indispensable in dental treatments.
Ceramics and Glass Industry: The ceramics industry harnesses zirconia's superior properties to produce high-performance ceramic components. It finds application in manufacturing ceramic knives, grinding media, cutting tools, and wear-resistant parts. Additionally, zirconia serves as a refractory material in the glass industry, lining furnace interiors and crucibles.
Aerospace and Defense:Zirconia's exceptional strength, resistance to high temperatures, and low thermal conductivity render it invaluable in aerospace and defense applications. It is utilized as a thermal barrier coating in turbine blades, engine components, and heat shields. Moreover, zirconia-based ceramics contribute to ballistic armor and protective shielding.
Biomedical and Healthcare: Zirconia plays a crucial role in biomedical applications, particularly in orthopedics and dentistry. It is employed in hip replacements, dental implants, and medical instruments due to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. Zirconia-based materials are also utilized in medical imaging equipment, including X-ray and CT scanner components.
Foundry and Refractory Materials: Zirconia finds utility in foundries as a mold material, owing to its ability to withstand high temperatures and thermal shock. Additionally, it is utilized in refractory materials for lining furnaces, kilns, and incinerators where elevated thermal resistance is essential.
In essence, zirconia's versatility, strength, high-temperature resistance, biocompatibility, and electrical properties contribute to its widespread adoption across diverse sectors. Its continued innovation and application across various industries underscore its significance as a multifaceted material driving technological advancements and enhancing product performance.
3. How are zirconia blocks made?
The production of dental zirconia blocks involves a meticulous process, encompassing several stages to ensure the creation of high-quality, precisely crafted restorations. Here's an in-depth look at the steps involved in manufacturing dental zirconia blocks:
1. Raw Material Selection and Preparation:
- The process commences with the careful selection of high-quality zirconium ore.
- The selected ore undergoes rigorous purification processes to remove impurities and ensure the purity of the zirconium.
- The purified zirconium is then combined with oxygen to form zirconium dioxide (ZrO2), also known as zirconia, the fundamental component of zirconia blocks.
2. Powder Preparation:
- The zirconium dioxide is processed into a fine powder, ensuring uniform particle size and distribution.
- Stabilizers, typically yttrium oxide (Y2O3), are added to the zirconia powder to enhance its stability and prevent phase transformation.
3. Isostatic Pressing:
- The zirconia powder mixture is placed in a rubber mold and subjected to isostatic pressing.
- Isostatic pressing applies uniform pressure from all directions, compacting the powder into a dense "green body" with consistent density and strength.
4. Pre-Sintering:
- The green zirconia body is pre-sintered in a furnace at moderate temperatures (around 1000°C - 1100°C).
- Pre-sintering imparts initial solidity to the zirconia block, making it easier to mill while retaining a slight porosity for milling accuracy.
5. CAD/CAM Milling:
- The pre-sintered zirconia block is digitally designed using CAD/CAM software based on patient-specific digital impressions.
- A precision milling machine carves the zirconia block into the desired shape and dimensions of the dental restoration with unparalleled accuracy.
6. Coloring (Optional):
- Prior to final sintering, the milled restoration may undergo optional coloring using specialized coloring liquids.
- These liquids permeate the porous structure of the pre-sintered zirconia, imparting desired shades and hues for enhanced aesthetics.
7. Final Sintering:
- The milled restoration undergoes a high-temperature sintering process in a furnace.
- Final sintering significantly increases the hardness and density of the zirconia, shrinking the restoration to its precise final dimensions.
8. Glazing and Polishing:
- Post-sintering, the restoration undergoes meticulous glazing and polishing processes.
- Glazing enhances the restoration's aesthetics and provides a smooth surface to minimize plaque accumulation, ensuring optimal oral hygiene.

Throughout the entire manufacturing process, stringent quality control measures are maintained to uphold the highest standards of precision, durability, and biocompatibility. From raw material selection to final finishing touches, each step is executed with utmost care to deliver superior-quality dental zirconia blocks tailored to meet the exacting demands of modern restorative dentistry.
4. What are the applications of zirconia blocks in dentistry?
Zirconia blocks, comprising zirconium dioxide, have become indispensable in dental restorations owing to their remarkable strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Let's delve into the primary applications of zirconia blocks in dentistry restoration:
1. Dental Crowns:
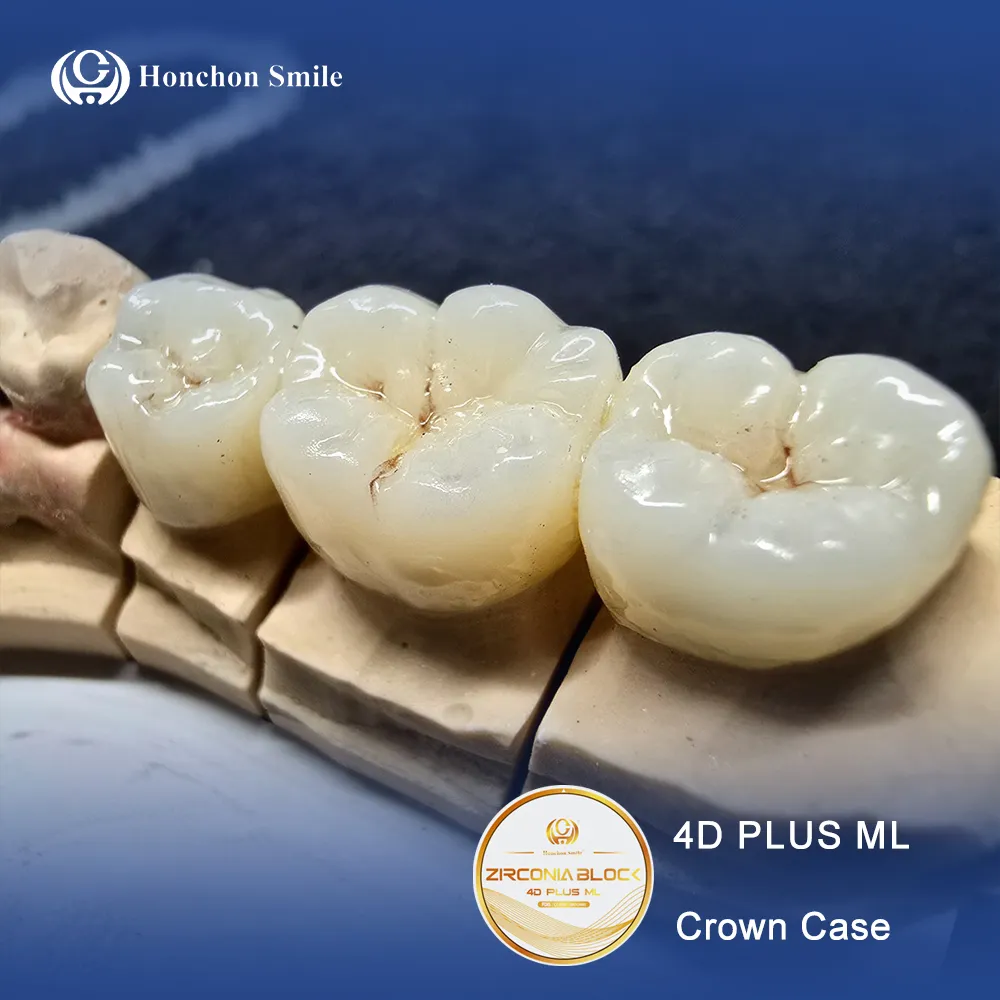 - Zirconia crowns are renowned for their exceptional strength and longevity, making them suitable for restoring damaged or weakened teeth.
- Zirconia crowns are renowned for their exceptional strength and longevity, making them suitable for restoring damaged or weakened teeth.
- These crowns offer superior resistance to fractures, particularly in high-stress areas like molars.
- Zirconia can be color-matched to natural teeth, ensuring seamless integration and an aesthetically pleasing outcome.
2. Bridges:
 - Zirconia bridges serve as effective replacements for one or more missing teeth, providing stability and functionality.
- Zirconia bridges serve as effective replacements for one or more missing teeth, providing stability and functionality.
- Due to its high fracture resistance and toughness, zirconia is an ideal material for bridges subjected to biting and chewing forces.
3. Implant Abutments:
 - Zirconia is commonly used in implant abutments, the connectors linking dental implants to artificial teeth.
- Zirconia is commonly used in implant abutments, the connectors linking dental implants to artificial teeth.
- Its biocompatibility and aesthetic properties make zirconia an optimal choice for creating natural-looking and durable abutments.
4. Veneers:
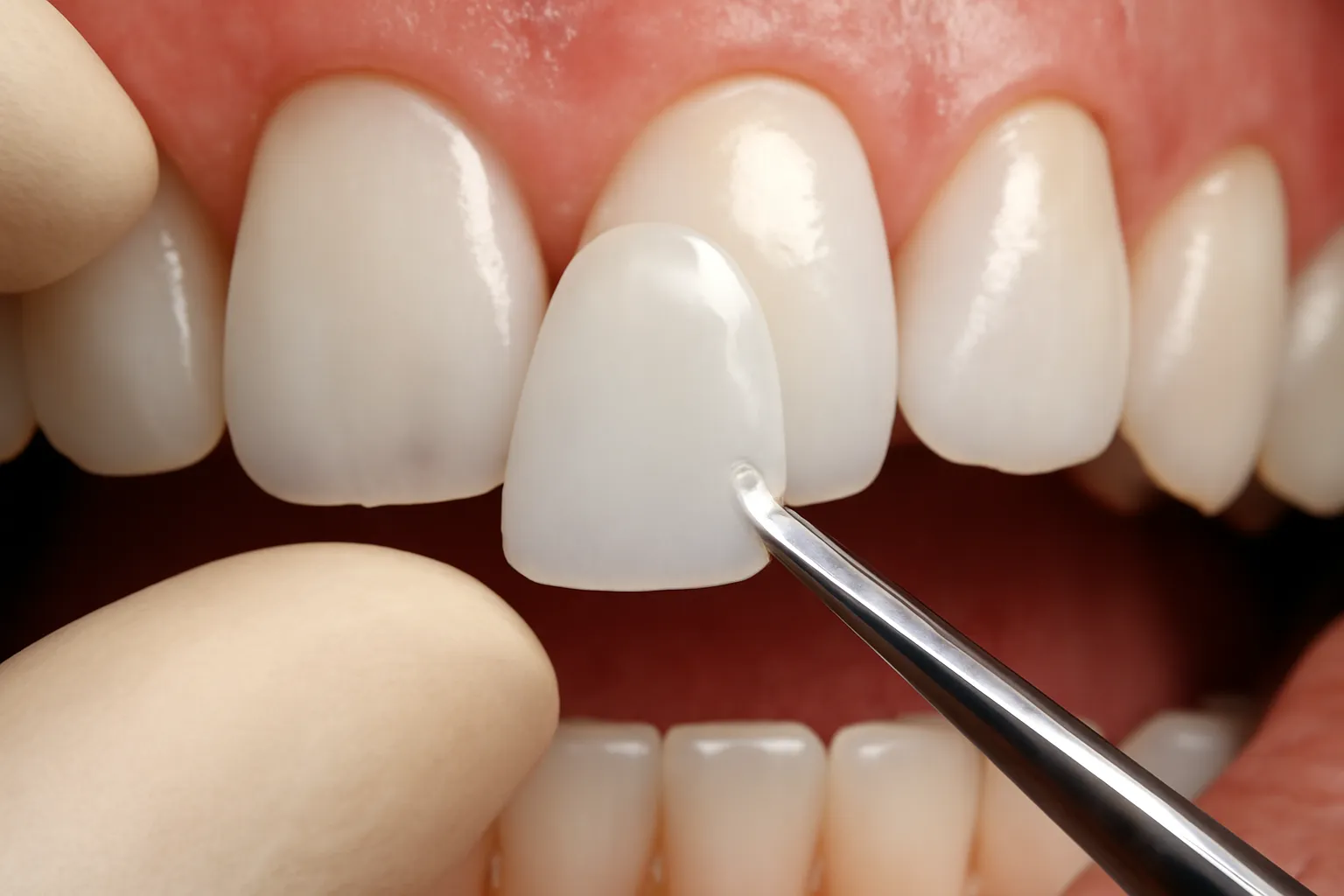 - Although less common than porcelain, zirconia veneers offer a viable option for enhancing the appearance of teeth.
- Although less common than porcelain, zirconia veneers offer a viable option for enhancing the appearance of teeth.
- Zirconia veneers are well-tolerated and can deliver satisfactory aesthetic results when bonded to the front surface of teeth.
5. Inlays and Onlays:
- Zirconia can be precisely milled to fabricate inlays and onlays, indirect restorations used to treat tooth decay or structural damage.
- Inlays and onlays made from zirconia offer durability and strength, striking a balance between fillings and crowns.
6. Full-Arch Restorations:
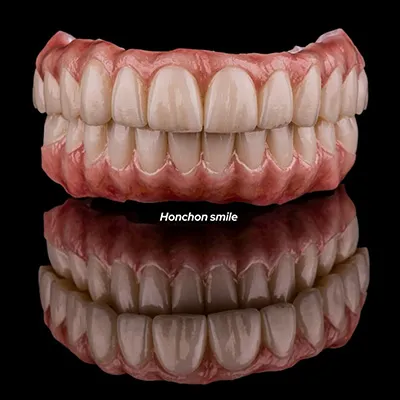 - For patients requiring complete upper or lower jaw tooth replacement, zirconia blocks are utilized to create full-arch prostheses.
- For patients requiring complete upper or lower jaw tooth replacement, zirconia blocks are utilized to create full-arch prostheses.
- High-strength zirconia ensures the longevity and stability of these comprehensive restorations.
To fabricate these restorations, dental professionals harness the power of CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology. This advanced technology enables precise digital design and milling of zirconia restorations, either within a dental laboratory or directly in the dental office. CAD/CAM technology ensures fast, accurate, and high-quality fabrication of zirconia restorations, revolutionizing the field of dental prosthetics.
5. How to choose the best dental zirconia block?
Choosing the best zirconia block for dental restorations involves considering various factors, including biocompatibility, mechanical properties, aesthetics, dental preparation requirements, longevity, and the skill of the dentist. Here's a detailed exploration of these factors and some top zirconia block options available:
Biocompatibility:
- Zirconia's exceptional biocompatibility minimizes the risk of adverse reactions or inflammation in the oral cavity. Its inert nature ensures compatibility with oral tissues, promoting healthy gum tissue around the restoration.
Mechanical Properties:
- Zirconia blocks come in different compositions, offering varying levels of strength and translucency. For posterior restorations requiring high strength, 3Y-TZP zirconia is often preferred. For anterior restorations where aesthetics are paramount, zirconia with enhanced translucency, such as 5Y-PSZ, may be preferable.
Aesthetics:
- Achieving lifelike aesthetics with zirconia restorations requires skillful fabrication and shading techniques. Blocks with high translucency and color customization options, like IPS e.max ZirCAD MT Multi and VITA YZ HT, are favored for natural-looking results.
Dental Preparation:
- Zirconia restorations typically require minimal tooth reduction, preserving more natural tooth structure. Dentists must ensure precise preparation to achieve proper fit and bonding of the restoration.
Longevity:
- The durability of zirconia restorations depends on various factors, including material quality, occlusal forces, and oral hygiene. High-quality zirconia blocks from reputable manufacturers, such as Ivoclar Vivadent's IPS e.max ZirCAD and Zirkonzahn's Prettau®, offer long-term reliability.
Skill of the Dentist:
- The success of zirconia restorations hinges on the dentist's expertise in treatment planning, preparation, and bonding. Dentists must be knowledgeable about zirconia properties and techniques to ensure optimal outcomes.
Top Zirconia Block Manufacturer Options:
- IPS e.max ZirCAD (Ivoclar Vivadent): Offers a range of blocks with different translucency levels and strengths for versatile applications.
- Lava™ Zirconia (3M): Known for its robustness and milling precision, suitable for posterior restorations.
- VITA YZ Solutions (VITA): Provides zirconia blocks with varying translucency and color options for aesthetic versatility.
- Prettau® and ICE Zirkon (Zirkonzahn): Ideal for full-arch restorations and areas with high masticatory load, offering exceptional strength and aesthetics.
- KATANA™ Zirconia (Kuraray Noritake): Multilayered blocks with natural translucency gradients, tailored for anterior restorations demanding high aesthetics.
Ultimately, the best zirconia block depends on the specific requirements of the dental case, including the location and type of restoration, aesthetic preferences, and the dentist's expertise. Consulting with a qualified dental professional or laboratory technician can help determine the most suitable zirconia block for each individual case.
Bonus: honchon smile
honchon smile has emerged as a prominent player in the dental industry, offering digital dental solutions characterized by affordability and quality. Here are some notable features that distinguish honchon smile in the market:
High Strength and Durability:
- honchon smile zirconia exhibits exceptional strength and fracture resistance, making it well-suited for dental restorations in high-stress areas like molars.
- The material's durability ensures long-lasting restorations, providing patients with reliable solutions that can withstand the rigors of daily use.
Aesthetics:
- honchon smile zirconia is renowned for its natural tooth-like color and translucency, contributing to aesthetically pleasing restorations that seamlessly blend with surrounding natural teeth.
- The availability of highly translucent zirconia blocks enables the creation of anterior restorations with superior aesthetics, meeting the demands of patients seeking optimal cosmetic outcomes.
Biocompatibility:
- Similar to other high-quality zirconia materials, honchon smile zirconia boasts excellent biocompatibility, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions or inflammation.
- Its inert nature ensures compatibility with oral tissues, promoting healthy gum tissues around the restoration and discouraging plaque accumulation.
- This biocompatibility enhances patient safety and comfort, fostering the success and longevity of dental restorations fabricated using honchon smile zirconia.
Affordability and Quality:
- honchon smile's emphasis on providing low-cost yet high-quality digital dental solutions appeals to buyers mindful of balancing cost and quality.
- The brand's commitment to delivering value-driven products enables dental professionals to access advanced materials without compromising on performance or reliability.
In summary, honchon smile has carved a niche in the dental industry by offering zirconia materials characterized by high strength, superior aesthetics, biocompatibility, and affordability. By prioritizing both quality and cost-effectiveness, honchon smile provides dental professionals with viable solutions for meeting the diverse needs of their patients while ensuring long-term success and satisfaction.
6. The difference between three different types of zirconia blocks.
Multilayer zirconia blocks, white zirconia blocks, and colored zirconia blocks each offer unique characteristics and applications in dental restorations.
These blocks feature layers of varying color and translucency, replicating the natural gradient of a tooth. By simulating the enamel-to-dentin transition, multilayer zirconia blocks deliver exceptionally natural-looking restorations. During manufacturing, layers of zirconia powder with different shades or translucency levels are compressed and sintered together. Primarily utilized in anterior restorations, where aesthetics are paramount, multilayer zirconia blocks provide a lifelike appearance that blends seamlessly with natural teeth.
Also known as monolithic or uncolored zirconia blocks, these are crafted from uniformly colored, high-purity white zirconia. While lacking the nuanced aesthetics of multilayer or colored variants, white zirconia blocks excel in strength and durability. They serve as ideal choices for posterior crowns or bridges, prioritizing resilience in high-stress areas. Additionally, they can be customized with coloring liquids post-milling but before final sintering to achieve specific aesthetic preferences.
Pre-colored during production to match various natural tooth shades, colored zirconia blocks offer a harmonious blend of aesthetics and strength. Although they may not achieve the same level of aesthetic depth as multilayer zirconia, they provide a uniform and pleasing appearance throughout the restoration. These blocks find utility when precise tooth shade matching is essential, catering to diverse patient preferences and aesthetic requirements.
In terms of applications, all three types of zirconia blocks find extensive use in a wide array of dental restorations, including crowns, bridges, veneers, and implant abutments. Selection among these variants is guided by factors such as patient-specific needs, restoration location within the oral cavity, and the desired balance between aesthetics and strength. Whether prioritizing lifelike appearance, durability, or color fidelity, dental professionals can leverage the versatility of zirconia blocks to achieve optimal treatment outcomes tailored to individual patient requirements.
7. Discuss the differences between zirconia materials and other materials?
Zirconia, a widely used material in dentistry, offers several advantages and some potential drawbacks. Let's explore the pros and cons of zirconia, particularly in comparison to metal ceramics.
Pros of Zirconia:
1. Aesthetics: Zirconia can be stained and glazed to match the color of natural teeth, providing highly aesthetic results. Its translucency and color-matching capabilities make it a popular choice for anterior restorations where aesthetics are paramount.
2. Biocompatibility: Zirconia is biocompatible, meaning it is non-toxic and does not harm living tissues. This makes it a safe option for dental restorations, reducing the risk of adverse reactions.
3. CAD/CAM: Zirconia restorations benefit from computer-aided design and manufacturing processes, ensuring precise fits and reducing chair time during adjustments and cementation. This technology enhances the overall efficiency and accuracy of the restoration process.
4. Strength and Durability: Zirconia is renowned for its strength and resistance to crack and fracture. This durability ensures the longevity of dental restorations, providing patients with reliable and long-lasting solutions for their oral health needs.
5. Conservative Tooth Preparation: Due to its strength, zirconia restorations require minimal tooth structure removal compared to other materials, preserving more of the natural tooth structure and promoting overall dental health.
Cons of Zirconia:
While the drawbacks of zirconia crowns are minimal, some considerations include:
- Friction Concerns: There have been concerns about potential friction against the tooth root and wearing down of opposing teeth due to the material's toughness. However, regular dental check-ups can help mitigate these risks.
- Initial Aesthetics Challenges: Initially, achieving aesthetically perfect results with zirconia crowns posed challenges, as only bone-white substructures were available. However, advancements in technology and materials have addressed this issue, allowing for more aesthetically pleasing outcomes.
Aesthetics Comparison: Zirconia vs. Metal Ceramics (PFM):
Both zirconia and metal ceramics are commonly used in dental restorations, each with its aesthetic qualities:
Zirconia:
- Translucency: Zirconia offers excellent translucency, closely mimicking natural teeth. Its high-translucency variants are particularly advantageous for anterior restorations where natural aesthetics are crucial.
- Color Matching: Zirconia can be color-matched to natural teeth, providing seamless integration with the patient's smile. Multilayer zirconia blocks further enhance color gradient, ensuring lifelike appearances.
- Metal-Free: Zirconia restorations are metal-free, eliminating the risk of dark metallic margins often associated with metal ceramics. This feature is beneficial for patients with metal sensitivities and enhances overall aesthetics.
Metal Ceramics (PFM):
- Porcelain Aesthetics: The porcelain component of metal ceramics can offer pleasing aesthetics, especially in terms of color and translucency.
- Metal Substructure: However, the metal substructure in PFMs can sometimes impact aesthetics. The opaque layer used to mask the metal may limit translucency, and visible metal margins can detract from the restoration's appearance, especially in cases of gum recession.
- Color Matching: While porcelain can be color-matched to natural teeth, achieving seamless color integration may require multiple layers of porcelain to hide the metal substructure, potentially affecting translucency and overall aesthetics.
In summary, while both zirconia and metal ceramics offer aesthetic benefits, zirconia tends to excel in terms of translucency, color matching, and metal-free composition. However, the final aesthetic outcome depends on various factors, including the dentist's expertise, patient preferences, and restoration location. Consulting with a dental professional is essential for making informed decisions about the most suitable restoration material for individual needs.
Zirconia and porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) are common materials used in dental restorations, each with its unique properties regarding durability and longevity.
Zirconia:
Zirconia is recognized for its exceptional strength and fracture toughness, making it a durable option for dental restorations. Its high strength has led to the increased use of monolithic zirconia restorations, which are entirely made from zirconia without the need for veneering porcelain.
When zirconia serves as a framework with a porcelain veneer, similar to PFMs, there's a risk of chipping or fracturing the veneer porcelain. Nonetheless, advancements in material science have introduced high-translucency zirconia, enabling its monolithic use and eliminating the risk of veneer fracture.
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Crowns:
PFM crowns have a long-established history of durability and longevity. The metal substructure provides high strength, while the fused porcelain delivers a natural tooth-like appearance.
However, PFMs aren't without issues. The porcelain veneer can chip or fracture, and over time, the metal substructure may rust.
Comparison:
Both zirconia and PFM crowns have demonstrated success in long-term dental restorations. Nonetheless, both carry the risk of veneer chipping or fracture. Monolithic zirconia crowns circumvent this risk by eliminating the need for a veneer altogether.
Both materials can cause wear on opposing teeth if the restoration's surface isn't properly polished or glazed. Some research suggests that zirconia may induce more wear on opposing enamel than PFM, but this remains a subject of ongoing debate.
In summary, both zirconia and PFMs offer commendable durability for dental restorations. The choice between them hinges on various factors such as restoration location, patient preference, cost considerations, and the dentist's expertise. Consulting with a dental professional is essential for determining the most suitable option for each case.
How Do The Costs Compare with Metal Ceramics?
The costs of dental restorations can vary significantly due to several factors, including the material used, restoration complexity, dentist fees, lab fees, and regional disparities in dental service costs. Here's a general comparison of zirconia and metal-ceramic restoration costs:
Zirconia Restorations:
Zirconia restorations typically incur higher costs than metal-ceramic ones due to several reasons:
Material Costs: Zirconia is pricier than metal-ceramic materials.
Laboratory Costs: The fabrication of zirconia restorations involves advanced CAD/CAM processes, which can increase lab expenses.
Durability: Despite higher upfront costs, zirconia restorations may offer better long-term value owing to their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
Metal-Ceramic (Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal or PFM) Restorations:
Metal-ceramic restorations usually cost less than zirconia ones due to:
Material Costs: The materials utilized in metal-ceramic restorations, while still providing adequate strength and aesthetics, are generally less expensive than zirconia.
Laboratory Costs: The fabrication process for PFM restorations is more established and typically less expensive, though it still necessitates skilled technicians for optimal results.
Popularity: PFMs have been a preferred choice for many years, contributing to their lower costs.
However, it's crucial to consider potential additional expenses down the line, such as the need for replacement due to porcelain chipping or aesthetic concerns.
In conclusion, while zirconia restorations typically entail higher upfront costs than metal-ceramic ones, the selection between the two shouldn't be solely based on cost. Other factors such as aesthetic requirements, restoration location, patient preferences, and overall treatment plan should also be taken into account. Consulting with a dental professional is advisable to determine the most suitable option for individual needs.












